3 AI Trends That Will Revolutionise Healthcare
Artificial Intelligence is becoming part of our reality in many more ways than it seems. AI is taking over not just our digital experiences, shopping on Amazon or watching TV-Series on Netflix, but becoming part of our lives across many industries, ranging from Automotive to Finance. One such industry is poised to benefit greatly from the use of AI, impacting our day-to-day lives (probably) more than any other: Healthcare.
AI research in medicine is growing rapidly. Healthcare AI projects attracted more investment than in any other sector of the global economy, with Healthcare being even called “the hottest AI category for deals”. This explosive growth is due to a wide variety of causes, starting with an ever-increasing adoption of big-data solutions and the need for technological solutions to adapt healthcare to crises such as the COVID-19 pandemic.
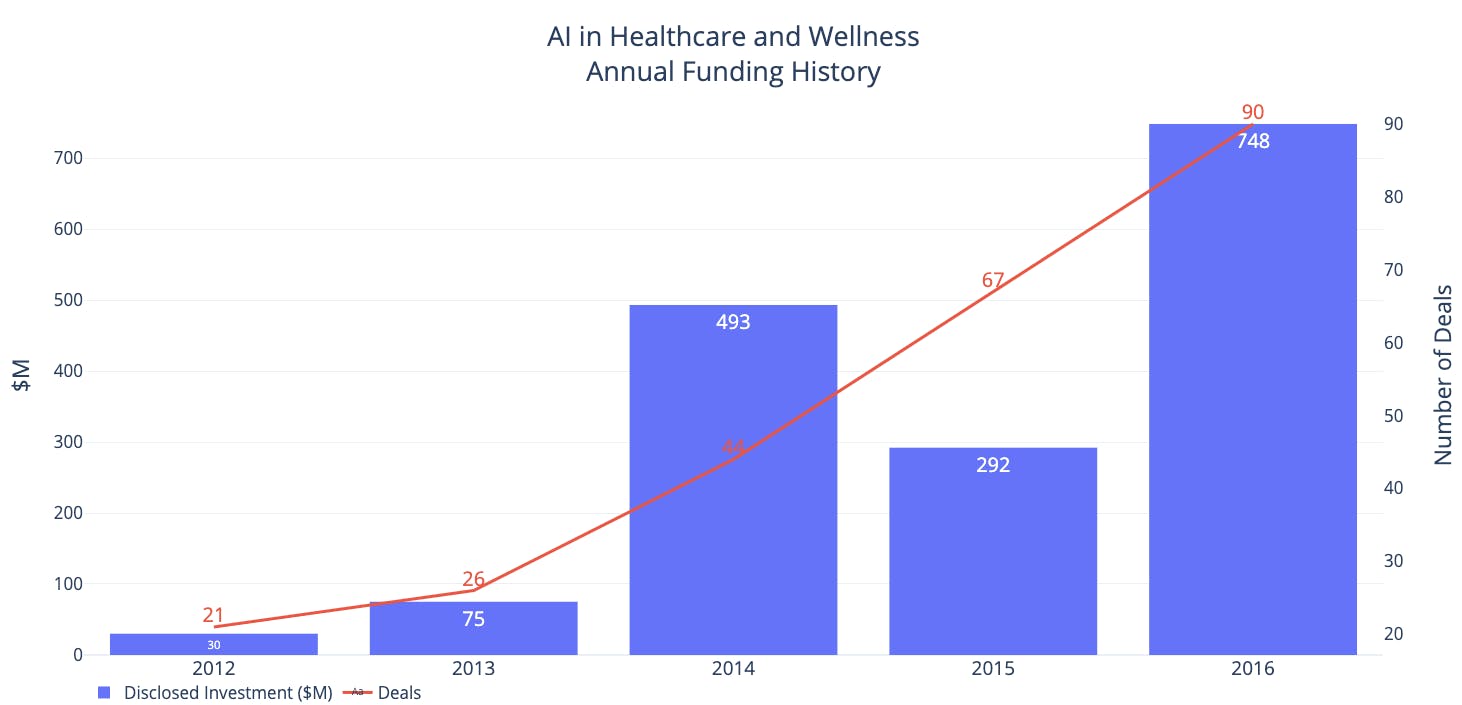
AI’s penetration in healthcare, a sector accounting $2,487.7 billion in 2019 in the U.S. alone, will have a significant impact in one of the key aspects for every country, the human wellbeing. In particular, AI will be able to assist medical experts such as doctors, nurses and medical personnel to assist them in more effectively detect early onsets of diseases and empower them to provide even more benefits for their patients.
Three trends, at least, are clearly being defined in the AI Healthcare space.
1. Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
The first trend might not seem entirely related to AI but is actually the most important one because of its impact on every other one. Electronic Health Records are digital records of a patient’s medical history, diagnoses and health journey throughout the years, acting basically like a digital version of doctors notes. These are usually collected first as notes during patient visits and then entered into a database that keeps information in a structured format.
According to the Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services, an Electronic Health Record (EHR) is “an electronic version of a patient's medical history, that is maintained by the provider over time, and may include all of the key administrative clinical data relevant to that persons care under a particular provider, including demographics, progress notes, problems, medications, vital signs, past medical history, immunizations, laboratory data, and radiology reports.”
There are currently many standards for record-keeping, but the most famous one, FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources), is becoming the leading protocol used by companies of the like of Google and Apple. FHIR uses a modern suite of APIs, HTTP-based RESTful protocols, HTML and CSS for UI integration and allows to use JSON, XML or RDF for data representation. One of its goals is to facilitate legacy healthcare systems to communicate with each other to easily provide information to medical providers and individuals. This is allowed on a wide variety of devices from computers to tablets and cell phones, and, more importantly, allows third-party developers to provide medical applications which can be easily integrated into existing systems.
With the current adoption of FHIR and the higher availability of electronic health records, medical providers like hospitals and private practices are being able to generate a huge amount of data. These consist of anonymised biographical data, diagnoses information, procedures, lab tests and much more. Such “explosion” of data is laying the foundation for AI’s penetration in Healthcare.
With these extremely rich datasets, companies are, and will be even more, able to apply Machine Learning techniques to extract insights from data, informing medical providers with key information. An example, strictly related to electronic health records, is shown by the use of Natural Language Processing algorithms to extract information from unstructured text. For instance, by running an NLP algorithm, we can extract clinical characteristics and diagnoses from the doctor’s notes, and store them in a structured format. These can be a list of diagnoses related to a specific patient, or a series of procedures to undertake.
2. Diagnosis Prediction
Another key area where AI will and is already revolutionising Healthcare is the area of early diagnosis prediction. This area consists of using Machine Learning models to predict a disease at its onset or even before it actually manifests itself.
This is achieved by training ML models with large quantities of labelled information, let the model find the relationship across that features that best predicts such disease, and then deploy the model “in the wild”.
These models are clearly dependent on large datasets to be able to effectively capture the underlying relationships between some patient features, such as age and their existing conditions, and the development of a target disease.
Luckily, the huge progress we’re witnessing with regards to Electronic Health Records is being able to feed large amounts of information to these models and, more importantly, will continue to do so as more patients enter the hospitals and medical facilities.
Many companies, from Google DeepMind to IBM Watson are using predictive models to detect diseases early on. IBM, in particular, has developed a system able to detect breast cancer with accuracies that rival radiologists.
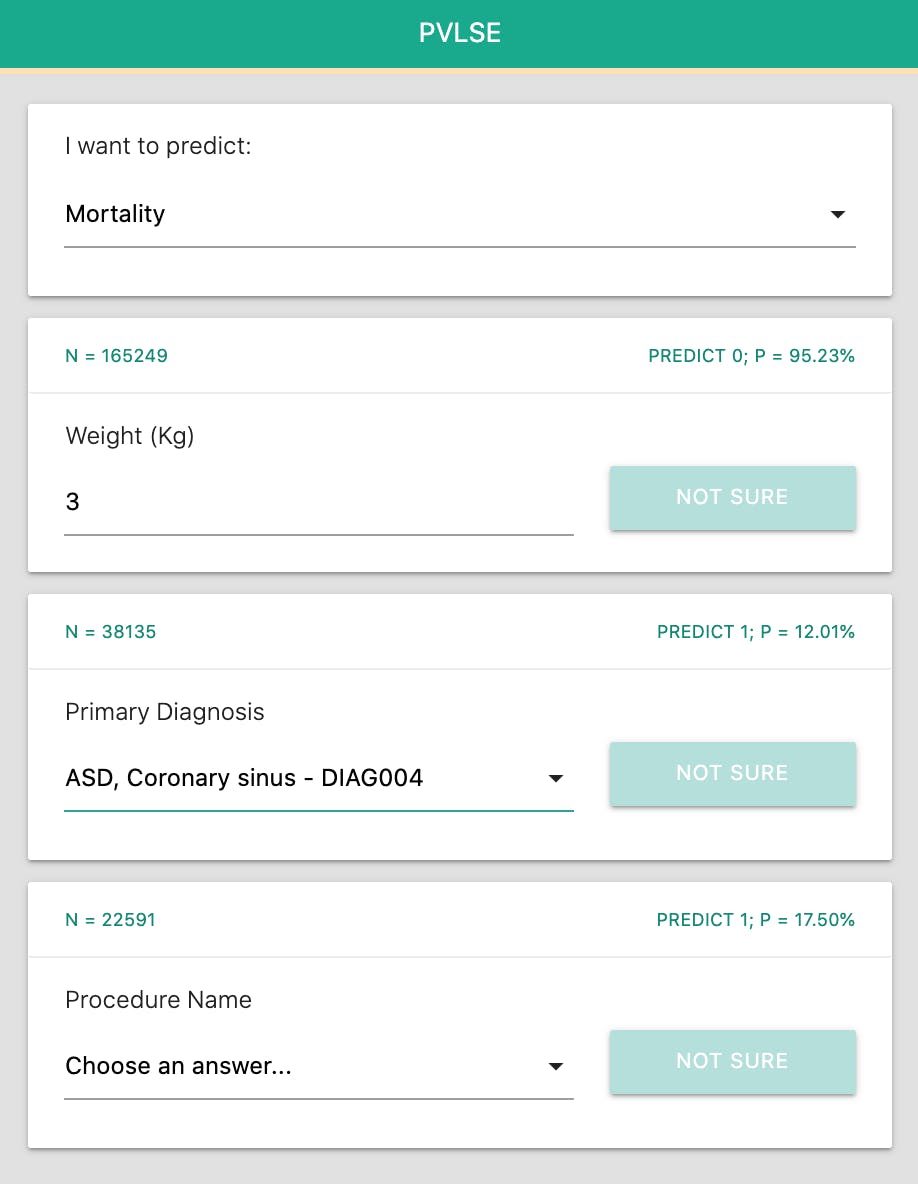
Over the past years, I also had the opportunity to develop several ML tools able to effectively detect diseases early on. One, called PVLSE, which has been commercialised through Alexandria Health, consists of an iPhone app running an ML model estimating the risk of children affected by cardiovascular issues to survive surgery using the same information that a surgeon would get (Age, Diagnoses, etc.).
By doing so, we were able to provide clinicians and surgeons with a “companion” able to empower them to take decisions driven partly by their experience and partly by a multitude of data coming from several countries, enriching their decision-making.
3. Telemedicine
Finally, through the use of these ML-based models, many companies are starting to develop solutions that allow patients to receive a level of treatment similar to going to a hospital, without leaving their home.
Companies like Babylon Health, have developed AI Chatbots able to provide medical guidance to patients. These chatbots receive messages from the users discussing about their present health issues, get that information as input and find the most likely disease that would cause such symptoms. This process, that in medical settings is called “Triage”, has been shown to be even more effective than when performed by doctors or nurses.
Another aspect of telemedicine is that of remote diagnoses not delivered by a “bot” but still a doctor. Basically, it consists of having a common doctor visit with the only difference that the doctor or nurse is remote and in contact through a video-streaming device, such as an iPad.
While this procedure might have been seen as odd and ineffective a few years ago, the significant changes that quickly happened over the past years changed a lot. The COVID-19 pandemic, in particular, accelerated the development of remote-medicine technologies substantially. This was due to the inability for doctors and family members to be in the same room of highly infective patients, especially at the onset of the pandemic, when the means of spreading of the virus were not yet clear.
Obstacles
Despite it might seem that these trends only provide positive impacts for society, there are a few different aspects that need to be addressed first before we are able to seize this opportunity entirely. First of all, AI-based technologies need to be accepted by medical experts and patients. Doctors, in particular, need to start becoming more comfortable with the presence of technological systems able to inform them of the next best action considering the data that these models were trained with. Doctors and medical professionals need to trust such models and be comfortable with these models not replacing them, but quite the opposite, empowering them with additional insights that are driven by having been trained with massive amounts of information, much larger than any doctor could have been trained with.
Secondly, best-practices for data privacy need to be set in place to guarantee the proper use of patients data and safeguard them from possible security breaches. Some best-practices, such as anonymization, have already been used extensively from medical providers, such as the NHS, and Data Science companies. However, the industry would benefit from more standardised set of procedures to guarantee data integrity and safe transmission of data across the different parties (patients, medical providers, family members, etc.).
Summary
To conclude, Healthcare is becoming one of the key sectors that AI is poised to revolutionise. Its trillion dollars economy clearly signals the scale of impact that AI can have, especially along three trends:
- Electronic Health Records
- Diagnosis Prediction
- Telemedicine
